Arithmetics
Variable
Made up of letters and digits
The first character must be a letter
The underscore ‘‘_’’ counts as a letter
Don’t begin variable names with underscore, however, since library routines often use such names
Upper and lower case letters are distinct, so x and X are two different names
Traditional C practice is to use lower case for variable names, and all upper case for symbolic constants
Constant
#include <stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
int main()
{
const int j = 30;
//j = 100; // not allowed to change value
printf("%f\n", PI);
return 0;
}
Arithmetic Operators
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 10, j = 100;
int r;
r = i + j;
printf("%d\n", r); // 110
r = i - j;
printf("%d\n", r); // -90
r = i * j;
printf("%d\n", r); // 1000
r = j / i;
printf("%d\n", r); // 10
printf("%f\n", (float) i / j); // 0.1
printf("%f\n", (float) (i / j)); // 0.0
r = i % 3;
printf("%d\n", r); // 1
i++;
printf("%d\n", i); // 11
j--;
printf("%d\n", j); // 99
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10;
a += 1; // a = a + 1
a -= 1; // a = a - 1
a *= 2; // a = a * 2
a /= 2; // a = a / 2
a %= 3; // a = a % 3
return 0;
}
Type Casting
implicit type casting, is performaed by compiler automatically
explict type casting, need to specify the cast operator
data type order: int < unsigned int <long < unsigned long < float < double
Two different types in an arithmetic expersion, the lower rank data type will be converted to the higher rank data type
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float a = 3.14;
int b;
b = a; // implicit conversion
printf("%d\n", b);
b = (int) a; // explicit conversion
printf("%d\n", b);
printf("%f\n", a + 1); // integer 1 is converted to float implicitly
return 0;
}
Bitwise Operators
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b;
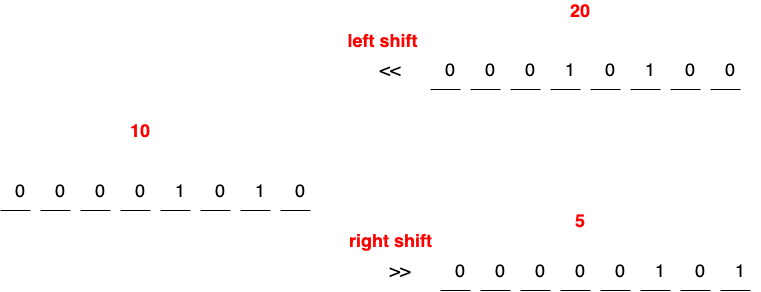
b = a << 2;
printf("%d\n", b); // 40
b = a >> 1;
printf("%d\n", b); // 5
a <<= 2; // a = a << 2
printf("%d\n", a); // 40
a >>= 1; // a = a >> 1
printf("%d\n", a); // 20
a = 5, b = 9;
printf("%d\n", a&b); // 1, 0101 and 1001
printf("%d\n", a|b); // 13, 0101 or 1001
printf("%d\n", a^b); // 12, 0101 exclusive or 1001
printf("%d\n", ~a); // -6, not 0101
return 0;
}
Reference