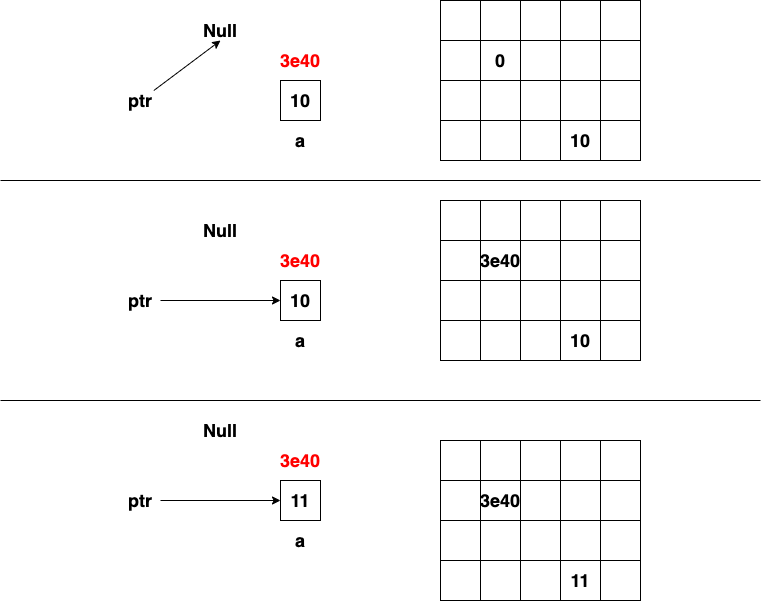
Pointer
Define a Pointer
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *ptr = NULL; // NULL is constant zero
printf("ptr: %p\n", ptr); // 0
int a = 10;
ptr = &a; // assign the address of variable a to ptr
// address
printf("a: %p\n", &a); // 5e83
printf("ptr: %p\n", ptr); // 5e83
// value
printf("a: %d\n", a); // 10
printf("*ptr: %d\n", *ptr); // 10
*ptr += 1;
// value
printf("a: %d\n", a); // 11
printf("*ptr: %d\n", *ptr); // 11
return 0;
}
Pass Pointers to Function by Reference
#include <stdio.h>
void change(int *p)
{
*p += 1;
}
int main()
{
int *ptr = NULL; // NULL is constant zero
int a = 10;
ptr = &a;
change(ptr);
// value
printf("a: %d\n", a); // 11
printf("*ptr: %d\n", *ptr); // 11
return 0;
}
Return a Pointer from a Function
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int * getInt()
{
int *p = NULL;
p = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
*p = rand()%10;
return p;
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
int *ptr = NULL; // NULL is constant zero
ptr = getInt();
printf("*ptr: %d\n", *ptr);
free(ptr);
return 0;
}
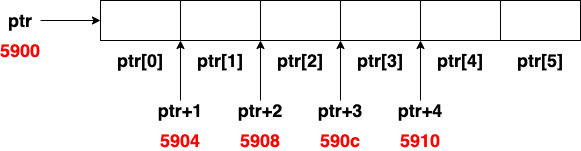
Represent a Array with a Pointer
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int *ptr = NULL;
// allocate the memory for 10 integers, let the pointer point to
// the address of the first element
ptr = malloc(sizeof(int)*10);
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
ptr[i] = i; // use pointer as an array
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
printf("%d\n", ptr[i]);
free(ptr); // release memory
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
Pointer Arithmetic
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int *ptr;
ptr = a;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
printf("%d, %d\n", i, *(ptr+i));
return 0;
}
Use Pointers in Function
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
// create an array with pointer
int * getArray(int size)
{
int *ptr;
ptr = (int*) malloc(size*sizeof(int));
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
ptr[i] = rand()%10;
return ptr;
}
// display array
void disp(int *ptr, int size)
{
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d: %d\n", i, ptr[i]);
}
// release memory
void removeArray(int *ptr)
{
free(ptr);
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
int *array;
array = getArray(10); // get array
disp(array, 10); // display array
removeArray(array); // release memory
return 0;
}
Memory Leak
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int getSum(int n)
{
// allocate memory
int ptr* = (int*)malloc(n*sizeof(int));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ptr[i] = rand()%10;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += ptr[i];
// not release memory
return sum;
}
int main()
{
while(true)
{
printf("%d\n", getSum(100));
}
return 0;
}
Pointers to Constants
#include <stdio.h>
void disp(const int *array, int size)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d\n", array[i]);
//array[0] = 10; // error
}
int main()
{
const int array[] = {0, 1, 2, 3};
disp(array, 4);
return 0;
}
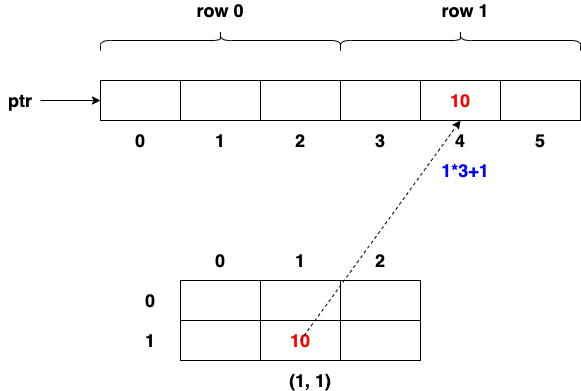
2D Array with 1D Pointer
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void display(int *array, int row, int column)
{
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < column; j++)
printf("%5d", array[i*column+j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int * getArray(int row, int column)
{
int *p;
p = (int *)malloc(row*column*sizeof(int));
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < column; j++)
p[i*column+j] = i*10+j;
return p;
}
int main()
{
int *ptr;
ptr = getArray(2, 3);
display(ptr, 2, 3);
free(ptr);
return 0;
}
Memory Operations
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void display(int *array, int size)
{
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%5d", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int * getArray(int size)
{
int *p;
p = (int *)malloc(size*sizeof(int));
return p;
}
int main()
{
// create an array and assign values
int *ptr;
ptr = getArray(10);
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
ptr[i] = i;
// create another array and copy values from ptr to copy
int *copy;
copy = getArray(10);
copy = (int *)realloc(copy, 20*sizeof(int)); // resize array
memcpy(copy, ptr, sizeof(int)*10);
// display array
display(ptr, 10);
display(copy, 20);
// free memory
free(ptr);
free(copy);
return 0;
}
Array of Pointer
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void setArray(int *array[], int r, int c)
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
for(j = 0; j < c; j++)
array[i][j] = i*10 + j;
}
void dispArray(int *array[], int r, int c)
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < c; j++)
printf("%10d", *(*(array+i)+j));
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int r = 3, c = 4;
int *array[r];
int i;
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
array[i] = (int*)malloc(c*sizeof(int));
setArray(array, r, c);
dispArray(array, r, c);
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
free(array[i]);
return 0;
}
2D Array with 2D Pointer
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void setArray(int **array, int r, int c)
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
for(j = 0; j < c; j++)
array[i][j] = i*10 + j;
}
void dispArray(int **array, int r, int c)
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < c; j++)
printf("%10d", *(*(array+i)+j));
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int r = 3, c = 4;
int **array;
// allocate two-dimensional array with a double pointer
array = (int **)malloc(r*sizeof(int *));
int i;
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
array[i] = (int*)malloc(c*sizeof(int));
setArray(array, r, c);
dispArray(array, r, c);
// free memory
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
free(array[i]);
free(array);
return 0;
}
Copy a 2D array represented by a 2D pointer, need to copy row by row
Copy the consecutive memory from the memory address of the first element may generate errors, since the rows may not allocated consecutive
String
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char *array;
size_t n = 80*sizeof(char);
array = (char *)malloc(n);
printf("Please enter your name:\n");
scanf("%s", array);
printf("%s, length is %lu\n", array, strlen(array));
return 0;
}
Pass Arguments to Program
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < argc; i++)
printf("Argument %d: %s\n", i, argv[i]);
return 0;
}