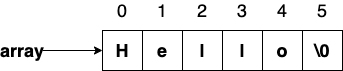
String
String with Array
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char array [] = "Hello"; // array has 6 characters
printf("Length: %lu\n", strlen(array)); // 5
printf("String: %s\n", array); // Hello
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
printf("|%c|\n", array[i]);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str[100];
printf("Enter a string: \n");
scanf("%s", str); // read the first token
printf("%s\n", str);
return 0;
}
//Hello World
//Hello
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str[100];
printf("Enter a string:\n");
fgets(str, sizeof(str), stdin); // read the whole line
printf("%s\n", str);
return 0;
}
//Hello World
//Hello World
//
String with Pointer
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char *getString()
{
char *str = "Hello World";
return str;
}
int main()
{
char *str = getString();
printf("Length: %lu\n", strlen(str)); // 5
printf("String: %s\n", str);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
char *getString()
{
char *str = (char *) malloc(100*sizeof(char));
scanf("%s", str); // read the first token
return str;
}
int main()
{
char *str = getString();
printf("Length: %lu\n", strlen(str)); // 5
printf("String: %s\n", str);
free(str);
return 0;
}
//Hello World
//Hello
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
char *getString()
{
char *str = (char *) malloc(100*sizeof(char));
fgets(str, 100, stdin);
return str;
}
int main()
{
char *str = getString();
printf("Length: %lu\n", strlen(str)); // 5
printf("String: %s\n", str);
free(str);
return 0;
}
//Hello World
//Hello World
//
string.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char *str1 = "Hello";
char *str2 = "Hello";
char *str3 = "World";
// strlen
printf("Length: %lu\n", strlen(str1)); // 5
// strcmp
// equal, 0; less than, negative integer; greater than, positive integer
printf("Compare: %d\n", strcmp(str1, str2)); // 0
printf("Compare: %d\n", strcmp(str1, str3)); // -15
//printf("String: %s\n", str);
// memcpy
char *str4 = (char *)malloc(strlen(str1)+1);
memcpy(str4, str1, strlen(str1)+1);
printf("Copy: %s\n", str4);
// strcat
char *str5 = (char *)malloc(strlen(str1)+strlen(str3)+1);
memcpy(str5, str1, strlen(str1));
strcat(str5, str3); // append str2 to str1
printf("Concatnate: %s\n", str5); // HelloWorld
// sub string
char *str6 = (char *) malloc(3);
memcpy(str6, &str5[5], 2);
str6[2] = '\0';
printf("Substring: %s\n", str6); // Wo
return 0;
}
Type Casting
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int getInteger()
{
printf("Enter an integer number:\n");
char str[100];
scanf("%s", str); // read the first token
return atoi(str);
}
double getDouble()
{
printf("Enter a double number:\n");
char *str = (char *) malloc(100*sizeof(char));
scanf("%s", str); // read the first token
double num = atof(str);
free(str);
return num;
}
int main()
{
int age = getInteger();
double pi = getDouble();
printf("%d\n", age);
printf("%f\n", pi);
return 0;
}
Change String
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
// pointer
char * str = "Hello"; // constant char data, do not free
//str[0] = 'W'; // bus error
str = "World";
printf("%s\n", str); //World
// array
char str2 [] = "Hello";
str2[0] = 'W';
//str2 = "World"; // not allowed
printf("%s\n", str2); //Wello
return 0;
}
Reference