In [4]:
from sktime.datasets import load_lynx
from sktime.utils.plotting import plot_series
y = load_lynx() # Series
plot_series(y)
Out[4]:
(<Figure size 1600x400 with 1 Axes>, <Axes: ylabel='Number of Lynx trappings'>)
from sktime.datasets import load_lynx
from sktime.utils.plotting import plot_series
y = load_lynx() # Series
plot_series(y)
(<Figure size 1600x400 with 1 Axes>, <Axes: ylabel='Number of Lynx trappings'>)
from sktime.datasets import load_longley
y, X = load_longley() # X, DataFrame, y, Series
for column in X.columns:
plot_series(X[column])
from sktime.datasets import load_arrow_head
X, y = load_arrow_head() # X, DataFrame, 211*1, y, numpy array
from sktime.datatypes import convert
# 211*1*251
# 211 records, each record is a time-series data with 251 observations
X = convert(X, from_type = 'nested_univ', to_type = 'numpy3D') # X, numpy array
import numpy as np
labels, counts = np.unique(y, return_counts=True)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
for label in labels:
ax.plot(X[y == label, 0, :][0])
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sktime.forecasting.base import ForecastingHorizon
# relative forecast horizon
fh = np.arange(1, 37)
# absolute forecast horizon
fh = ForecastingHorizon(pd.PeriodIndex(pd.date_range("1961-01", periods=36, freq="M")), is_relative=False)
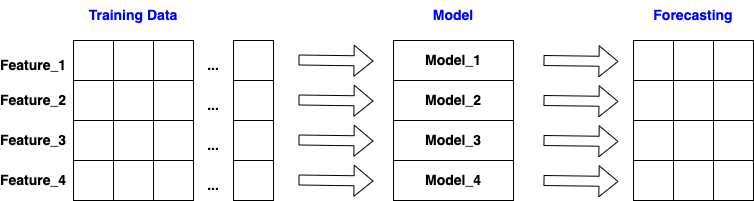
from sktime.forecasting.vecm import VECM
forecaster = VECM()
forecaster.get_class_tags()
{'scitype:y': 'multivariate',
'ignores-exogeneous-X': False,
'capability:pred_int': True,
'handles-missing-data': False,
'y_inner_mtype': 'pd.DataFrame',
'X_inner_mtype': 'pd.DataFrame',
'requires-fh-in-fit': False,
'X-y-must-have-same-index': True,
'enforce_index_type': None,
'fit_is_empty': False,
'python_version': None,
'python_dependencies': 'statsmodels',
'univariate-only': False}
from sktime.registry import all_estimators
all_estimators("forecaster", as_dataframe=True)
all_estimators("forecaster", filter_tags={"scitype:y": ["univariate"]}, as_dataframe=True)
all_estimators(filter_tags={"scitype:y": ["multivariate", "both"]}, as_dataframe=True)
all_estimators(filter_tags={"capability:pred_int": True}, as_dataframe=True)