Count
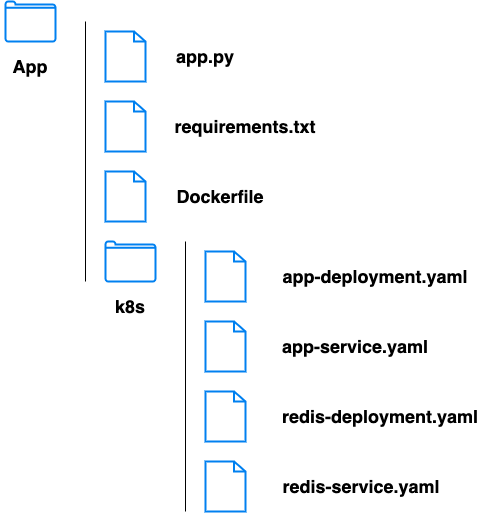
# app.py
import os
import time
import redis
from flask import Flask
def get_ip():
return os.getenv('MYREDIS_HOST', 'localhost')
app = Flask(__name__)
cache = redis.Redis(host=get_ip(), port=6379)
def get_hit_count():
retries = 5
while True:
try:
return cache.incr('hits')
except redis.exceptions.ConnectionError as exc:
if retries == 0:
raise exc
retries -= 1
time.sleep(0.5)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
count = get_hit_count()
return 'Hello from Docker! I have been seen {} times.\n'.format(count)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
# requirements.txt
flask
redis
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.7-alpine
WORKDIR /code
ENV FLASK_APP=app.py
ENV FLASK_RUN_HOST=0.0.0.0
RUN apk add --no-cache gcc musl-dev linux-headers
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
EXPOSE 5000
COPY . .
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
# app-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: webapp-deployment
labels:
app: webapp
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: webapp # let deployment know which pod for this deployment
template: # configuration for pods
metadata:
labels:
app: webapp # each pod has a unique name, but pods can share the same label
spec:
containers: # containers in a pod, usually add one container per pod
- name: webapp
image: lchenlangley/count # pull image from local
imagePullPolicy: Never
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
env:
- name: MYREDIS_HOST
value: redis-service
# app-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: webapp-service # service name accessed by app
spec:
selector:
app: webapp # match the pod labels
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 5000 # service port
targetPort: 5000 # pod port
# redis-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-deployment
labels:
app: redis
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis # let deployment know which pod for this deployment
template: # configuration for pods
metadata:
labels:
app: redis # each pod has a unique name, but pods can share the same label
spec:
containers: # containers in a pod, usually add one container per pod
- name: redisdb
image: redis:alpine # pull image from Docker Hub
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
# redis-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-service # service name accessed by app
spec:
selector:
app: redis # match the pod labels
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 6379 # service port
targetPort: 6379 # pod port
Minikube
# select Kubernetes/minikube on Docker Desktop
# 1. Start minikube
minikube start
eval $(minikube docker-env) # point to inside of Minikube container
# 2. Create image in the registry of the Minikube container
docker build -t lchenlangley/count .
# 3. Deploy app on K8s cluster or minikube
# kubectl get all, search service name
kubectl create -f k8s # k8s is the directory of yaml files
# 4. Expore service port to user
kubectl port-forward svc/webapp-service 8000:5000 # [external port]:[service port]
# 5. Access app
http://localhost:8000/
# Cleaning Up
kubectl delete -f k8s
Reference