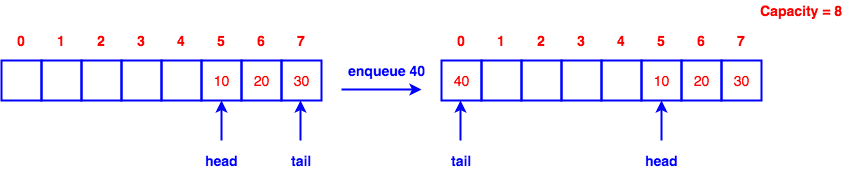
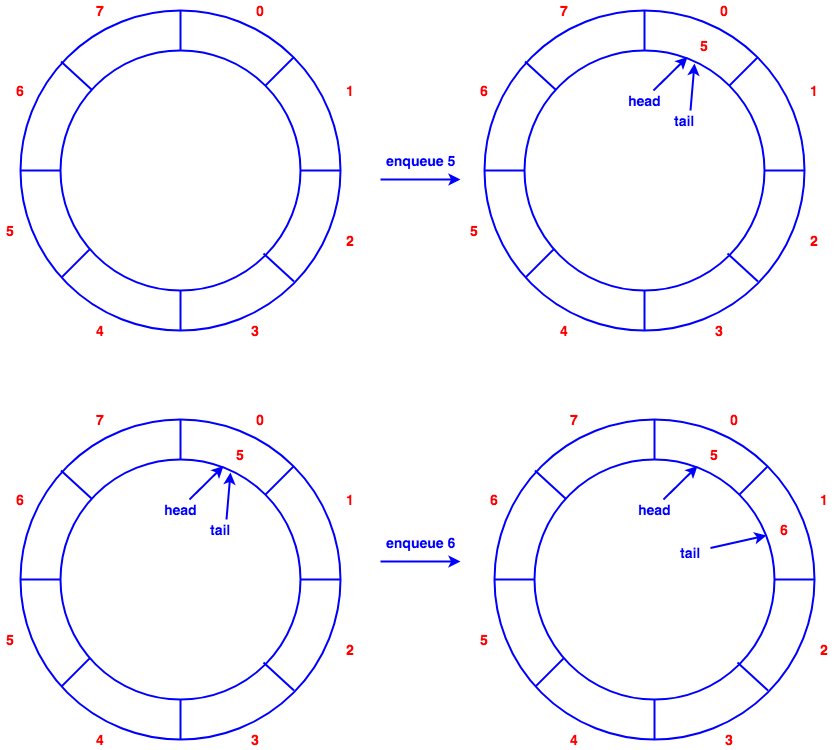
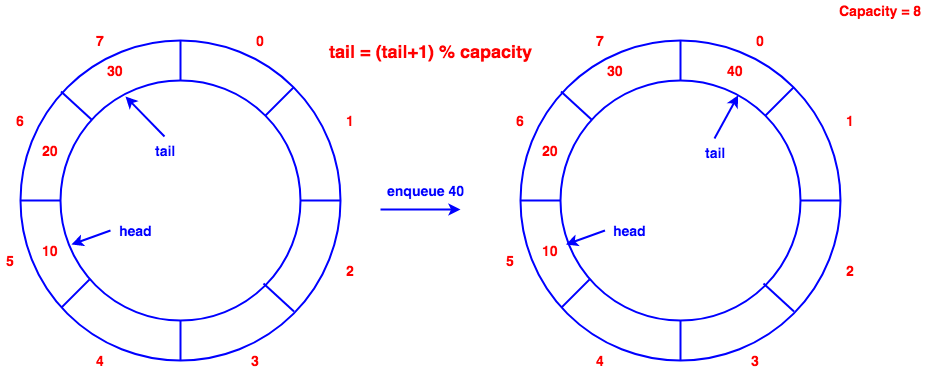
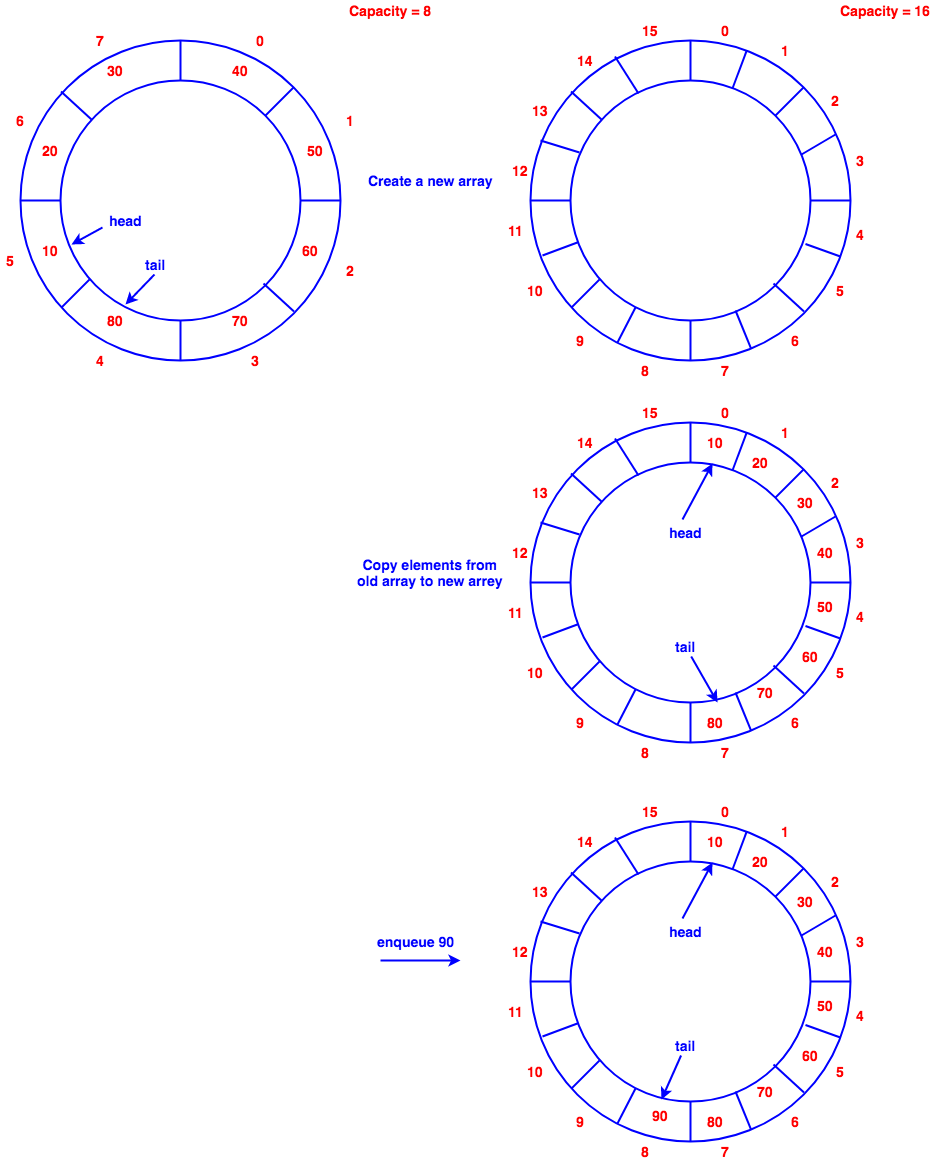
Queue
Queue is a linear structure, the order is First In First Out (FIFO)
Operations
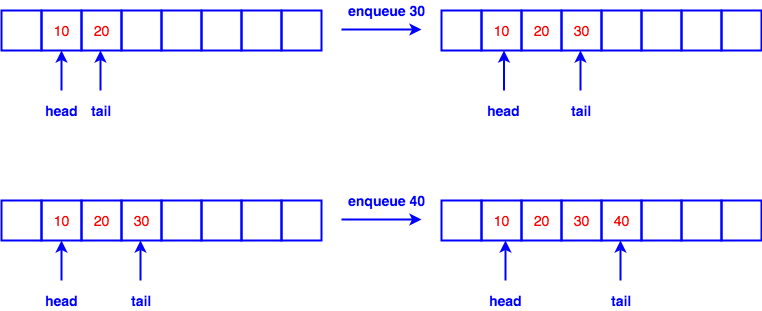
enqueue(), insert element at the tail
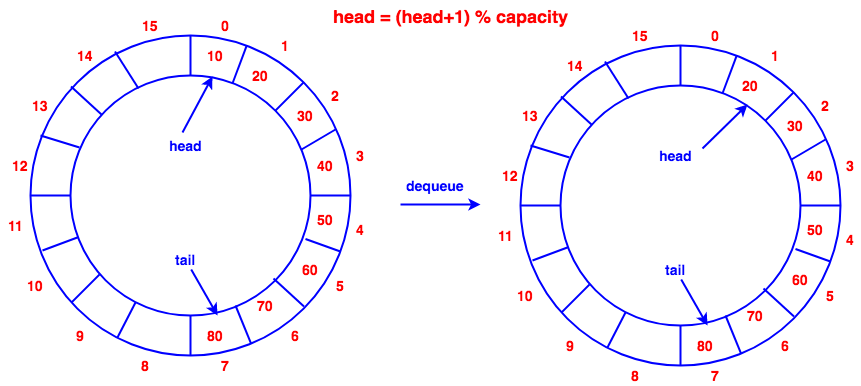
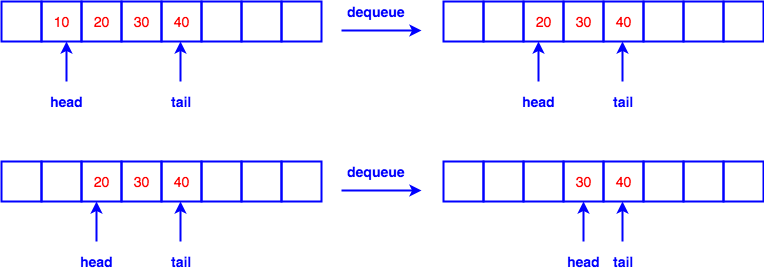
dequeue(), delete element at the head
front(), return element at head
rear(), return element at rear
Implementation with array
Implementation with list
- # QueueModule.py
- #!/usr/bin/python3
- class Queue(object):
- def __init__(self):
- self.items = []
-
- def isEmpty(self):
- return len(self.items) == 0
-
- def enqueue(self, v):
- try:
- self.items.insert(0,v)
- return True
- except Exception as e:
- return False
-
- def dequeue(self):
- try:
- item = self.items.pop()
- return item
- except Exception as e:
- return None
-
- def size(self):
- return len(self.items)
-
- def front(self):
- if self.size() == 0:
- return None
- return self.items[self.size()-1]
-
- def rear(self):
- if self.size() == 0:
- return None
- return self.items[0]
-
- def __str__(self):
- s = 'rear ->'
-
- output = []
-
- for item in self.items:
- output.append(str(item))
-
- s += '->'.join(output)
-
- s += '-> front'
-
- return s
-
- #!/usr/bin/python3
- from QueueModule import Queue
-
- def main():
- q = Queue()
-
- q.enqueue(4)
- q.enqueue('dog')
- q.enqueue(True)
-
- print(q) # rear ->True->dog->4-> front
- print(q.size()) # 3
-
- print(q.dequeue()) # 4
-
- print(q.front()) # dog
- print(q.rear()) # True
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
-
Implementation with linked list
- #!/usr/bin/python3
- """ A model containing Node class """
- import copy
-
- __author__ = "Lin Chen"
- __version__ = "0.1"
-
- class Node:
- """Single node with double pointers pointing to its previous node and the node after it"""
-
- def __init__(self, data):
- """Initialize a Node
-
- Args:
- data : data saved in the node
- """
- self._data = data
- self._prev = None
- self._next = None
-
- @property
- def data(self):
- return self._data
-
- @data.setter
- def data(self, d):
- self._data = d
-
- @data.deleter
- def data(self):
- del self._data
-
- @property
- def next(self):
- return self._next
-
- @next.setter
- def next(self, n):
- self._next = n
-
- @next.deleter
- def next(self):
- del self._next
-
- @property
- def prev(self):
- return self._prev
-
- @prev.setter
- def prev(self, n):
- self._prev = n
-
- @prev.deleter
- def prev(self):
- del self._prev
-
- def __str__(self):
- return str(self._data)
-
Double Linked List
- #!/usr/bin/python
- """ A modeule containing List class"""
-
- from NodeModule import Node
-
- class List:
- """Linked List class with a pre-defined Node class"""
-
- def __init__(self):
- """Initialize a List
- """
- self._head = None
- self._tail = None
- self._count = 0
-
- def getSize(self):
- """Return the size of the list
-
- Returns:
- int : size of the list
- """
- return self._count
-
- def access(self, index):
- """Access a node with its index
-
- Args:
- index: index of a specified node
-
- Returns:
- Node: a pointer of the specified node if the specifid node exists; None, otherwise
- """
- if index < 0 or index > self._count-1:
- return None
-
- # access the front node
- if index == 0:
- return self._head
-
- # access the tail node
- if index == self._count-1:
- return self._tail
-
- if index <= self.getSize()/2: # access the first half
- current = self._head
- for i in range(index):
- current = current.next
- return current
- else: # access the second half
- current = self._tail
- for i in range(self.getSize()-index-1):
- current = current.prev
- return current
-
- return None
-
- def insert(self, index, v):
- """Insert a valude to make the list maintain ascending order
-
- Args:
- v : data which can be saved in a node
-
- Returns:
- Node: True, if the value is inserted succefully; False, otherwise
- """
- if index < 0 or index > self._count:
- return False
-
- n = Node(v) # create a node
-
- # insert a node into an empty list
- if self.getSize() == 0:
- self._head = n
- self._tail = n
- self._count += 1
- return True
-
- # insert a node in the front
- if index == 0:
- n.next = self._head
- self._head.prev = n
- self._head = n
- self._count += 1
- return True
-
- # insert a node at the end
- if index == self.getSize():
- n.prev = self._tail
- self._tail.next = n
- self._tail = n
- self._count += 1
- return True
-
- if index <= self.getSize()/2:
- current = self._head
- for i in range(index-1):
- current = current.next
- n.next = current.next
- n.prev = current
- current.next.prev = n
- current.next = n
- self._count += 1
- return True
- else:
- current = self._tail
- for i in range(self.getSize()-index-1):
- current = current.prev
- n.next = current
- n.prev = current.prev
- current.prev.next = n
- current.prev = n
- self._count += 1
- return True
-
- return False
-
- def delete(self, index):
- """Delete a valude located at a specific location in the list
-
- Args:
- index (int): location of deletion, 0 is the location before the first element, 1 is the location after the first element
-
- Returns:
- boolean: the value of removed node, if the node is deleted succefully; None, otherwise
- """
- if index < 0 or index > self._count-1:
- return None
-
- if index == 0:
- n = self._head
- self._head = self._head.next
- self._head.prev = None
- self._count -= 1
- return n
-
- if index == self._count-1:
- n = self._tail
- self._tail = self._tail.prev
- self._tail.next = None
- self._count -= 1
- return n
-
- if index <= self._count/2:
- current = self._head
- for i in range(index-1):
- current = current.next
- n = current.next
- current.next = current.next.next
- current.next.prev = current
- self._count -= 1
- return n
- else:
- current = self._tail
- for i in range(self.getSize()-index-2):
- current = current.prev
- n = current.prev
- current.prev = current.prev.prev
- current.prev.next = current
- self._count -= 1
- return n
-
- return None
-
- def __str__(self):
- """Convert the list to a string
-
- Returns:
- string : a string represents the list
- """
- if self.getSize() == 0:
- return "Empty"
-
- current = self._head
- output = []
-
- while current is not None:
- output.append(str(current))
- current = current.next
-
- return " -> ".join(output)
-
Queue
- #!/usr/bin/python
-
- from ListModule import List
-
- class Queue(List):
- def __init__(self):
- List.__init__(self)
-
- def enqueue(self, v):
- """insert element at the tail
-
- Args:
- v : data which can be saved in a node
-
- Returns:
- boolean: True, if the value is inserted succefully; False, otherwise
- """
- return self.insert(self.getSize(), v)
-
- def dequeue(self):
- """delete a node from the front
-
- Args:
- index (int): location of deletion, 0 is the location before the first element, 1 is the location after the first element
-
- Returns:
- Node: a pointer of the delete node if the queue is not empty; None, otherwise
- """
- return self.delete(0)
-
- def front(self):
- """access the first node in the queue
-
- Returns:
- Node: a pointer of the first node if the queue is not empty; None, otherwise
- """
- return self.access(0)
-
- def rear(self):
- """access the tail node in the queue
-
- Returns:
- Node: a pointer of the tail node if the queue is not empty; Noen, otherwise
- """
- return self.access(self._count-1)
-
Test
- #!/usr/bin/python
-
- from QueueModule import Queue
-
- def main():
- q = Queue()
-
- # enqueue
- q.enqueue(10)
- q.enqueue(20)
- q.enqueue(15)
- q.enqueue(30)
- q.enqueue(40)
- print(q)
-
- # front
- print(q.front().data)
-
- # rear
- print(q.rear().data)
-
- # dequeue
- n = q.dequeue() # 10
- print(n.data) # the value of remove node
- print(q)
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
-
Queue Sample
A operating system
E-mail system