Stack
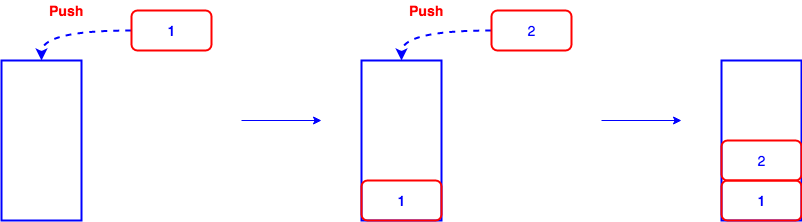
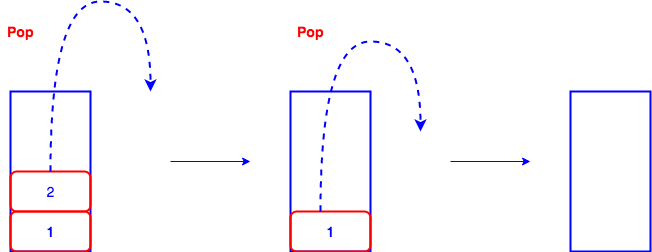
Stack is a linear data structure, the order is FILO (First In Last Out)
Operations
push(), add an element to the top of a stack
pop(), remove the top element from a stack
top(), returns top element of stack
Implementation with list
# StackModule.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import copy
class Stack(object):
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def isEmpty(self):
return len(self.items) == 0
def push(self, element):
try:
self.items.append(element)
return True
except Exception as e:
return False
def pop(self):
try:
return self.items.pop()
except Exception as e:
return None
def peek(self):
try:
return self.items[len(self.items)-1]
except Exception as e:
return None
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
def __str__(self):
output = []
items = copy.copy(self.items)
items.reverse()
for item in items:
output.append(str(item))
return " -> ".join(output)
#!/usr/bin/python3
from StackModule import Stack
def main():
s = Stack()
s.push(1)
s.push(2)
s.push(3)
s.push(4)
print('Hello')
print(s) # 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
p = s.pop()
print(p) # 4
print(s) # 3 -> 2 -> 1
print(s.isEmpty()) # False
print(s.peek()) # 3
print(s.size()) # 3
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Implementation with linked list
# NodeModule.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
""" A model containing Node class """
import copy
__author__ = "Lin Chen"
__version__ = "0.1"
class Node:
"""Single node in a data structure"""
def __init__(self, data):
"""Initialize a Node
Args:
data : data saved in the node
"""
self._data = data
self._next = None
@property
def data(self):
return self._data
@data.setter
def data(self, d):
self._data = d
@data.deleter
def data(self):
del self._data
@property
def next(self):
return self._next
@next.setter
def next(self, n):
self._next = n
@next.deleter
def next(self):
del self._next
def __copy__(self):
#print('Call copy ...')
return Node(copy.deepcopy(self._data))
def __str__(self):
return str(self._data)
# ListModule.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
""" A modeule containing Sorted List class
The data structure is a linked list of nodes, in which the elements
has been sorted by ascending order"""
import copy
from NodeModule import Node
class List(object):
"""Linked List class with a pre-defined Node class"""
def __init__(self):
"""Initialize a List
"""
self._head = None
self._count = 0
def isEmpty(self):
"""Check if the list is empty
Args:
None
Returns:
boolean : True, if list is empty; False, otherwise
"""
return self._count == 0
def getSize(self):
"""Return the size of the list
Returns:
int : size of the list
"""
return self._count
def insert(self, index, v):
"""Insert a valude to a specific location in the list
Args:
index (int): location of insertion, 0 is the location before the first element, 1 is the location after the first element
v : data which can be saved in a node
Returns:
boolean: True, if the value is inserted succefully; False, otherwise
"""
if index < 0 or index > self._count:
return False
n = Node(v) # create a node
if index == 0:
n.next = self._head
self._head = n
self._count += 1
return True
current = self._head
for i in range(index-1):
current = current.next
n.next = current.next
current.next = n
self._count += 1
return True
def delete(self, index):
"""Delete a valude located at a specific location in the list
Args:
index (int): location of deletion, 0 is the location before the first element, 1 is the location after the first element
Returns:
Node: return the deleted node if it is deleted successfully; False, otherwise
"""
if index < 0 or index > self._count-1:
return None
if index == 0:
n = copy.copy(self._head)
self._head = self._head.next
self._count -= 1
return n
current = self._head
for i in range(index-1):
current = current.next
n = copy.copy(current.next)
current.next = current.next.next
self._count -= 1
return n
def __str__(self):
"""Convert the list to a string
Returns:
string : a string represents the list
"""
if self.isEmpty():
return "Empty"
current = self._head
output = []
while current is not None:
output.append(str(current))
current = current.next
return " -> ".join(output)
# StackModule.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
""" A module containing Stack class which is implmented by linked list"""
from ListModule import List
class Stack(List):
"""Stack, FILO linear data structure"""
def __init__(self):
List.__init__(self)
def push(self, v):
self.insert(0, v)
def pop(self):
return self.delete(0)
#!/usr/bin/python3
from StackModule import Stack
def main():
s = Stack()
s.push(1)
s.push(2)
s.push(3)
s.push(4)
print(s) # 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
p = s.pop()
print(p) # 4
print(s) # 3 -> 2 -> 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Applications
Balancing of symbols
Infix to Postfix /Prefix conversion
Redo-undo features at many places like editors
Forward and backward feature in web browsers



