Static Methods and Class Methods
Instance Methods
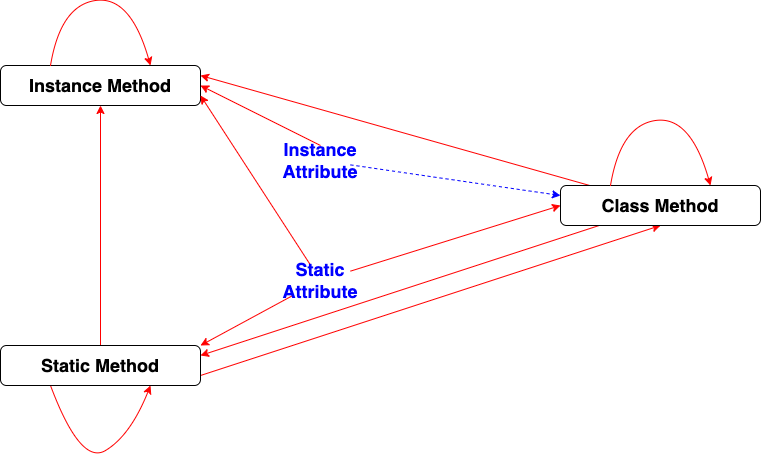
- Can access instance methods, instance attributes, static methods, static attributes, class methds
Static Methods
- Is bound to the class and not the object of the class, can’t access or modify the class state
- Can access other static methods, static attributes
- Cannot access instance methods, instance attributes, class methods
Class Methods
- Is bound to the class and not the object of the class, can modify a class state that would apply across all the instances of the class
- Can access other class methods, static methods, static attributes
- Can access instance attributes when changing class state by calling __init__
- Cannot access instance methods
Instance Method
class A(object):
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
def instance(self):
return self.value
def instance2(self):
self.instance()
a = A(10)
a.instance2()
Static Method
# define static method by staticmethod()
class A(object):
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
def static():
return 'S ...'
static = staticmethod(static)
# call by class
A.static()
# call by instance
#a = A(10)
#a.static()
# define static method by decorator
class A(object):
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@staticmethod
def static():
return 'S ...'
# call by class
A.static()
# call by instance
#a = A(10)
#a.static()
# static method calls static method
class A(object):
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@staticmethod
def static():
return 'S ...'
@staticmethod
def static2():
return A.static()
# call by class
A.static2()
# call by instance
a = A(10)
a.static2()
# instance method call static method
class A(object):
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@staticmethod
def static():
return 'S ...'
def instance(self):
return A.static()
# call by instance
a = A(10)
a.instance()
# static variable can be accessed by static method and instance method
class A(object):
count = 0 # static variable
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@staticmethod
def static():
return A.count
def instance(self):
return A.count
a = A(10)
a.static()
a.instance()
Class Method
# define class method
class A(object):
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@classmethod
def classmeth(cls):
return 'C ...'
# call by class
A.classmeth()
# call by instance
#a = A(10)
#a.classmeth()
# class method can call static variable and static method
class A(object):
count = 0
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@staticmethod
def static():
return A.count
@classmethod
def classmeth(cls):
return A.static()
@classmethod
def classmeth2(cls):
return A.count
A.classmeth()
A.classmeth2()
# class method call class method
class A(object):
count = 0
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@staticmethod
def static():
return A.count
@classmethod
def classmeth(cls):
return A.static()
@classmethod
def classmeth2(cls):
return cls.classmeth()
A.classmeth2()
# static method call class method
class A(object):
count = 0
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@staticmethod
def static():
return A.classmeth()
@classmethod
def classmeth(cls):
return A.count
A.static()
# instance method call class method
class A(object):
count = 0
def __init__(self, v):
self.value = v
@classmethod
def classmeth(cls):
return A.count
def instance(self):
return A.classmeth()
a = A(10)
a.instance()
# create new instance with class method
class A(object):
def __init__(self, v):
print('Call init ...')
self.value = v
@classmethod
def classmeth(cls, value): # call __init__
return cls(value)
def instance(self):
return self.value
a = A(10) # call __init__
a = A.classmeth(100) # call __init__, create a new instance
a.instance() # 100
a.classmeth(200) # call __init__, return an instance, not change original instance
a.instance() # 100
Reference