pygrib
Installation
Format
GRIB file format is designed for storing and distributing weather data
Keys
- identificationOfOriginatingGeneratingCentre, identification of originating generating centre
- date, year, month, day, hour, minute, second
- longitudeOfFirstGridPointInDegrees, latitudeOfFirstGridPointInDegrees, longitudeOfLastGridPointInDegrees, latitudeOfLastGridPointInDegrees
- regular_II, grid type
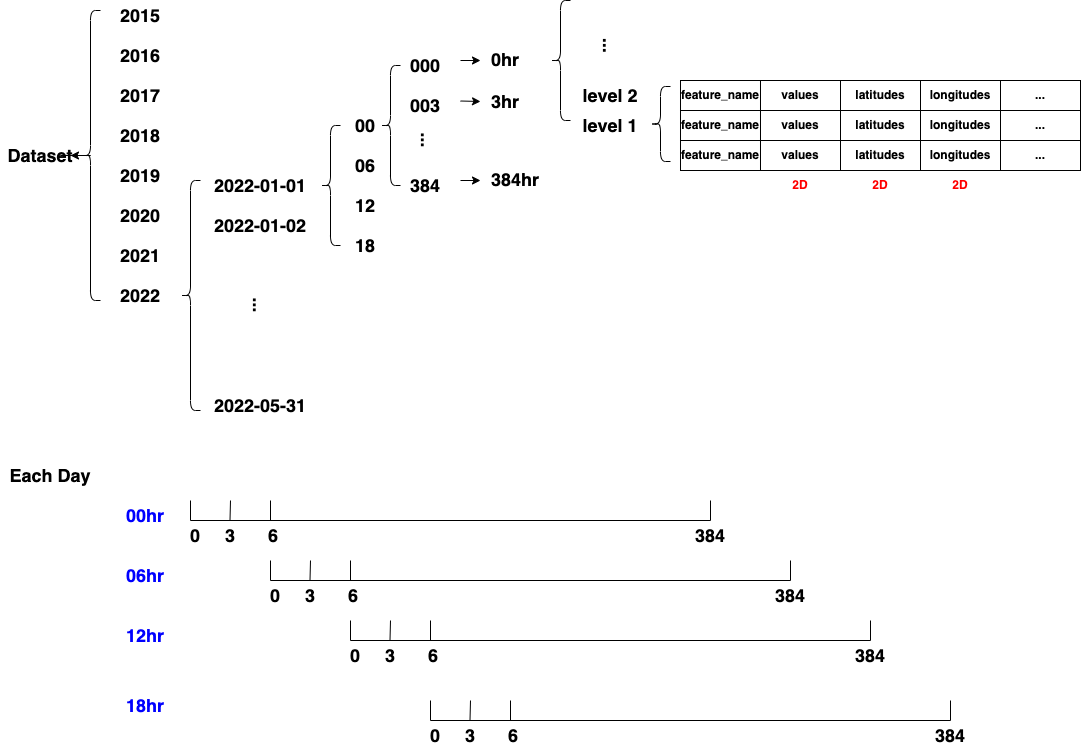
NOAA Forecast Repository
Multiple records for a name in a grib2 file, have different level values
pygrib._pygrib.open
import pygrib
# open a grib2 file
grbs = pygrib.open('gfs.0p25.2022010100.f000.grib2')
# variables
grbs.messages # number of messages
grbs.messagenumber # current position
grbs.name # grib file
# move the pointer to the 100th record
grbs.seek(100)
# rewind to the beginning
grbs.rewind()
# get the current position of the pointer
grbs.tell()
# get N messages from current position
msgs = grbs.read(10) # a list of pygrib._pygrib.gribmessage
# read all messages from the current position
msgs = grbs.read()
# get the message at the current position
msg = grbs.readline() # pygrib._pygrib.gribmessage
# get the nth message
grbs.message(10)
# select
grbs.select() # get all messages in a grib2 file
grbs.select()[0].keys() # get keys
grbs.select()[index] # get a message, row
# [m.key_name for m in grbs.select()] # get values of a key, column
selected_grbs = grbs.select(year = 2022, name = 'Temperature') # select messages by key values
selected_grbs = grbs(year = 2022, name = 'Temperature')
# get features
set([m.name for m in grbs.select()])
# close the pointer
grbs.close()
class pygrib.index
# create an index with specified keys
grbindx=pygrib.index('gfs.0p25.2022010100.f000.grib2','name','level')
# search messages with keys
selected_grbs=grbindx.select(name='Temperature',level=1)
# close
grbindx.close()
pygrib._pygrib.gribmessage
# get the value of a key of a message
grb = grbs.select()[0]
kyes = grb.keys()
# grb.key_name
# grb['key_name']
grb.name # feature name
grb.data() # values, latitudes, longitudes
grb.latlons() # latitudes (-90, 90), longitudes (0, 360)
Visualization
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = grb.values
grb = grbs.select()[0]
lons = np.linspace(float(grb['longitudeOfFirstGridPointInDegrees']), \
float(grb['longitudeOfLastGridPointInDegrees']), int(grb['Ni']) )
lats = np.linspace(float(grb['latitudeOfFirstGridPointInDegrees']), \
float(grb['latitudeOfLastGridPointInDegrees']), int(grb['Nj']) )
#cs = plt.contourf(data, extend='both')
c = plt.pcolormesh(lons, lats, data, cmap ='Blues')
plt.colorbar()
To DataFrame
import pandas as pd
# define weather features in need
features = ['Temperature', 'Pressure', 'Relative humidity']
# fetch values, latitudes, longitudes for each feature
feature_container = {}
for grb in grbs:
for feature in features:
if grb.name == feature:
feature_container[grb.name] = grb.data()
features.remove(feature) # use the first message for each feature
# convert dict of feature:(values, latitudes, longitudes) to a Pandas DataFrame
data = feature_container[list(feature_container.keys())[0]]
lat_size = data[0].shape[0]
lon_size = data[0].shape[1]
feature_names = feature_container.keys()
records = []
for lat_index in range(lat_size):
for lon_index in range(lon_size):
record = {}
for feature_name in feature_names:
record[feature_name] = feature_container[feature_name][0][lat_index][lon_index]
record['latitude'] = feature_container[feature_name][1][lat_index][lon_index]
record['longitude'] = feature_container[feature_name][2][lat_index][lon_index]
records.append(record)
df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(records)
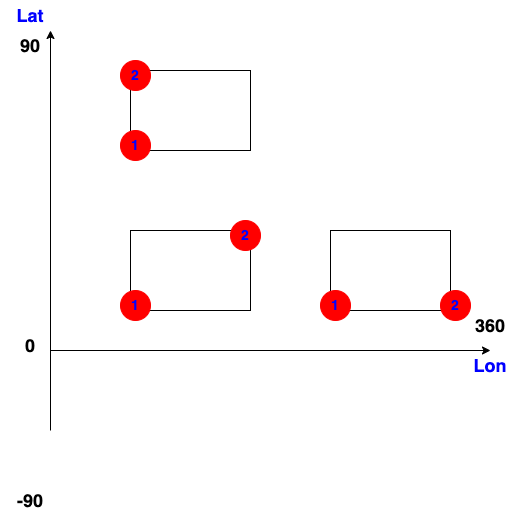
Cropping
p1 = (1, 1) # lat1, lon1
p2 = (2, 2) # lat2, lon2
sub_data = grb.data(lat1=p1[0], lat2=p2[0], lon1=p1[1], lon2=p2[1])
if sub_data[0].shape[0] <= 0:
raise Exception('Sub-region illegal')
np.mean(sub_data[0])
Reference